# agent-squad
**Repository Path**: joey2022/agent-squad
## Basic Information
- **Project Name**: agent-squad
- **Description**: 多智能体框架
- **Primary Language**: Python
- **License**: Apache-2.0
- **Default Branch**: bedrock-classifier-profile
- **Homepage**: None
- **GVP Project**: No
## Statistics
- **Stars**: 0
- **Forks**: 1
- **Created**: 2025-07-30
- **Last Updated**: 2025-07-30
## Categories & Tags
**Categories**: Uncategorized
**Tags**: None
## README
Multi-Agent Orchestrator 
Flexible and powerful framework for managing multiple AI agents and handling complex conversations.




灵活、轻量级的开源框架,用于编排多个 AI 代理以处理复杂的对话。
## 🔖 特性
- 🧠 智能意图分类 — 根据上下文和内容将查询动态路由到最合适的代理。
- 🔤 双语言支持 — 在 Python 和 TypeScript 中完全实现。
- 🌊 灵活的代理响应 — 支持来自不同代理的流式处理和非流式处理响应。
- 📚 上下文管理 — 维护和利用多个座席之间的对话上下文,以实现连贯的交互。
- 🔧 可扩展的架构 — 轻松集成新代理或自定义现有代理以满足您的特定需求。
- 🌐 通用部署 — 在任何地方运行 – 从 AWS Lambda 到您的本地环境或任何云平台。
- 📦 预构建的代理和分类器 — 提供各种即用型代理和多个分类器实现。
## 什么是 Agent Squad ❓
Agent Squad 是一个灵活的框架,用于管理多个 AI 代理和处理复杂的对话。它智能地路由查询并跨交互维护上下文。
该系统提供用于快速部署的预构建组件,同时还允许轻松集成自定义代理和对话消息存储解决方案。
这种适应性使其适用于广泛的应用程序,从简单的聊天机器人到复杂的 AI 系统,适应不同的需求并有效扩展。
## 🏗️ 高级架构流程图
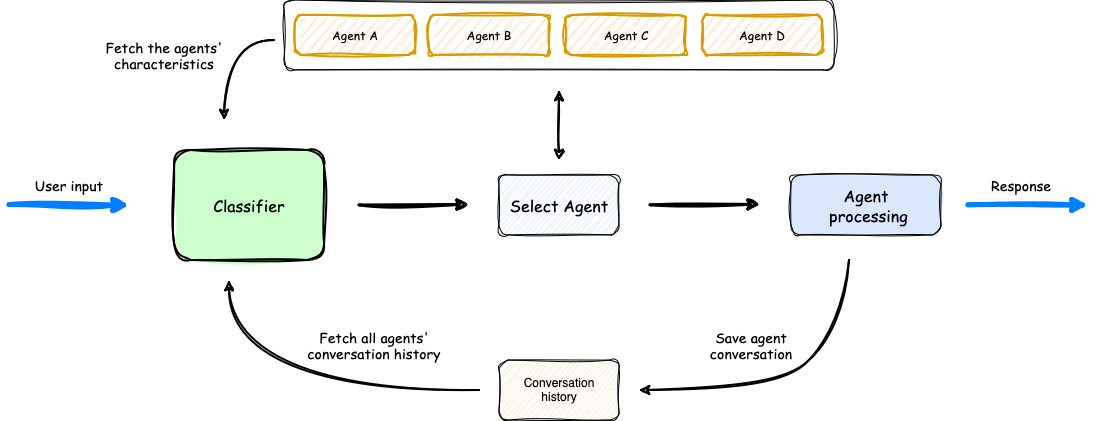
1.该过程从用户输入开始,由 Classifier 进行分析。
2.分类器利用 Agents' Characteristics 和 Agents' Conversation history 来为任务选择最合适的代理。
3.选择代理后,它将处理用户输入。
4.然后,编排器保存对话,更新代理的对话历史记录,然后将响应传回给用户。
## 💬 Demo App
To quickly get a feel for the Multi-Agent Orchestrator, we've provided a Demo App with a few basic agents. This interactive demo showcases the orchestrator's capabilities in a user-friendly interface. To learn more about setting up and running the demo app, please refer to our [Demo App](https://awslabs.github.io/multi-agent-orchestrator/deployment/demo-web-app/) section.
在下面的屏幕录像中,我们演示了使用 6 个专用代理的演示应用程序的扩展版本:
- Travel Agent:由 Amazon Lex 机器人提供支持
- Weather Agent:利用带有查询 open-meteo API 的工具的 Bedrock LLM Agent
- Restaurant Agent:作为 Amazon Bedrock Agent 实施
- Math Agent:利用带有两个工具的 Bedrock LLM Agent 来执行数学运算
- 技术代理:一个 Bedrock LLM 代理,旨在回答有关技术主题的问题
- Health Agent:专注于解决与健康相关的查询的 Bedrock LLM Agent
观看系统在不同主题之间无缝切换上下文,从预订航班到查看天气、解决数学问题和提供健康信息。 请注意如何为每个查询选择合适的代理,即使有简短的后续输入,也能保持连贯性。
该演示重点介绍了该系统处理复杂的多轮对话的能力,同时保留上下文并利用各个领域的专业代理。

## 🚀 示例和快速入门
Check out our [documentation](https://awslabs.github.io/multi-agent-orchestrator/) for comprehensive guides on setting up and using the Multi-Agent Orchestrator!
## 🌟 Use cases and implementations
Discover creative implementations and diverse applications of the Multi-Agent Orchestrator:
- **[From 'Bonjour' to 'Boarding Pass': Multilingual AI Chatbot for Flight Reservations](https://community.aws/content/2lCi8jEKydhDm8eE8QFIQ5K23pF/from-bonjour-to-boarding-pass-multilingual-ai-chatbot-for-flight-reservations)**
This article demonstrates how to build a multilingual chatbot using the Multi-Agent Orchestrator framework. The article explains how to use an **Amazon Lex** bot as an agent, along with 2 other new agents to make it work in many languages with just a few lines of code.
### TypeScript Version
#### Installation
```bash
npm install multi-agent-orchestrator
```
#### Usage
The following example demonstrates how to use the Multi-Agent Orchestrator with two different types of agents: a Bedrock LLM Agent with Converse API support and a Lex Bot Agent. This showcases the flexibility of the system in integrating various AI services.
```typescript
import { MultiAgentOrchestrator, BedrockLLMAgent, LexBotAgent } from "multi-agent-orchestrator";
const orchestrator = new MultiAgentOrchestrator();
// Add a Bedrock LLM Agent with Converse API support
orchestrator.addAgent(
new BedrockLLMAgent({
name: "Tech Agent",
description:
"Specializes in technology areas including software development, hardware, AI, cybersecurity, blockchain, cloud computing, emerging tech innovations, and pricing/costs related to technology products and services.",
streaming: true
})
);
// Add a Lex Bot Agent for handling travel-related queries
orchestrator.addAgent(
new LexBotAgent({
name: "Travel Agent",
description: "Helps users book and manage their flight reservations",
botId: process.env.LEX_BOT_ID,
botAliasId: process.env.LEX_BOT_ALIAS_ID,
localeId: "en_US",
})
);
// Example usage
const response = await orchestrator.routeRequest(
"I want to book a flight",
'user123',
'session456'
);
// Handle the response (streaming or non-streaming)
if (response.streaming == true) {
console.log("\n** RESPONSE STREAMING ** \n");
// Send metadata immediately
console.log(`> Agent ID: ${response.metadata.agentId}`);
console.log(`> Agent Name: ${response.metadata.agentName}`);
console.log(`> User Input: ${response.metadata.userInput}`);
console.log(`> User ID: ${response.metadata.userId}`);
console.log(`> Session ID: ${response.metadata.sessionId}`);
console.log(
`> Additional Parameters:`,
response.metadata.additionalParams
);
console.log(`\n> Response: `);
// Stream the content
for await (const chunk of response.output) {
if (typeof chunk === "string") {
process.stdout.write(chunk);
} else {
console.error("Received unexpected chunk type:", typeof chunk);
}
}
} else {
// Handle non-streaming response (AgentProcessingResult)
console.log("\n** RESPONSE ** \n");
console.log(`> Agent ID: ${response.metadata.agentId}`);
console.log(`> Agent Name: ${response.metadata.agentName}`);
console.log(`> User Input: ${response.metadata.userInput}`);
console.log(`> User ID: ${response.metadata.userId}`);
console.log(`> Session ID: ${response.metadata.sessionId}`);
console.log(
`> Additional Parameters:`,
response.metadata.additionalParams
);
console.log(`\n> Response: ${response.output}`);
}
```
### Python Version
#### Installation
```bash
# Optional: Set up a virtual environment
python -m venv venv
source venv/bin/activate # On Windows use `venv\Scripts\activate`
pip install multi-agent-orchestrator
```
#### Usage
Here's an equivalent Python example demonstrating the use of the Multi-Agent Orchestrator with a Bedrock LLM Agent and a Lex Bot Agent:
```python
import os
import asyncio
from multi_agent_orchestrator.orchestrator import MultiAgentOrchestrator
from multi_agent_orchestrator.agents import BedrockLLMAgent, LexBotAgent, BedrockLLMAgentOptions, LexBotAgentOptions, AgentCallbacks
orchestrator = MultiAgentOrchestrator()
class BedrockLLMAgentCallbacks(AgentCallbacks):
def on_llm_new_token(self, token: str) -> None:
# handle response streaming here
print(token, end='', flush=True)
tech_agent = BedrockLLMAgent(BedrockLLMAgentOptions(
name="Tech Agent",
streaming=True,
description="Specializes in technology areas including software development, hardware, AI, \
cybersecurity, blockchain, cloud computing, emerging tech innovations, and pricing/costs \
related to technology products and services.",
model_id="anthropic.claude-3-sonnet-20240229-v1:0",
callbacks=BedrockLLMAgentCallbacks()
))
orchestrator.add_agent(tech_agent)
# Add a Lex Bot Agent for handling travel-related queries
orchestrator.add_agent(
LexBotAgent(LexBotAgentOptions(
name="Travel Agent",
description="Helps users book and manage their flight reservations",
bot_id=os.environ.get('LEX_BOT_ID'),
bot_alias_id=os.environ.get('LEX_BOT_ALIAS_ID'),
locale_id="en_US",
))
)
async def main():
# Example usage
response = await orchestrator.route_request(
"I want to book a flight",
'user123',
'session456'
)
# Handle the response (streaming or non-streaming)
if response.streaming:
print("\n** RESPONSE STREAMING ** \n")
# Send metadata immediately
print(f"> Agent ID: {response.metadata.agent_id}")
print(f"> Agent Name: {response.metadata.agent_name}")
print(f"> User Input: {response.metadata.user_input}")
print(f"> User ID: {response.metadata.user_id}")
print(f"> Session ID: {response.metadata.session_id}")
print(f"> Additional Parameters: {response.metadata.additional_params}")
print("\n> Response: ")
# Stream the content
async for chunk in response.output:
if isinstance(chunk, str):
print(chunk, end='', flush=True)
else:
print(f"Received unexpected chunk type: {type(chunk)}", file=sys.stderr)
else:
# Handle non-streaming response (AgentProcessingResult)
print("\n** RESPONSE ** \n")
print(f"> Agent ID: {response.metadata.agent_id}")
print(f"> Agent Name: {response.metadata.agent_name}")
print(f"> User Input: {response.metadata.user_input}")
print(f"> User ID: {response.metadata.user_id}")
print(f"> Session ID: {response.metadata.session_id}")
print(f"> Additional Parameters: {response.metadata.additional_params}")
print(f"\n> Response: {response.output.content}")
if __name__ == "__main__":
asyncio.run(main())
```
These examples showcase:
1. The use of a Bedrock LLM Agent with Converse API support, allowing for multi-turn conversations.
2. Integration of a Lex Bot Agent for specialized tasks (in this case, travel-related queries).
3. The orchestrator's ability to route requests to the most appropriate agent based on the input.
4. Handling of both streaming and non-streaming responses from different types of agents.
📚 Featured Articles
We're excited to share contributions that showcase the power and flexibility of the Multi-Agent Orchestrator. Check out this featured article:
From 'Bonjour' to 'Boarding Pass': Multilingual AI Chatbot for Flight Reservations
Create a global flight reservation chatbot in minutes! This tutorial walks you through building a multilingual chatbot using the Multi-Agent Orchestrator framework. Learn to effortlessly chain AI agents for instant language processing and booking across multiple languages. Transform complex, multi-step processes into a polyglot flight reservation system.
## 🤝 Contributing
We welcome contributions! Please see our [Contributing Guide](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/awslabs/multi-agent-orchestrator/main/CONTRIBUTING.md) for more details.
## 📄 LICENSE
This project is licensed under the Apache 2.0 licence - see the [LICENSE](https://raw.githubusercontent.com/awslabs/multi-agent-orchestrator/main/LICENSE) file for details.
## 📄 Font License
This project uses the JetBrainsMono NF font, licensed under the SIL Open Font License 1.1.
For full license details, see [FONT-LICENSE.md](https://github.com/JetBrains/JetBrainsMono/blob/master/OFL.txt). 
