# vedo
**Repository Path**: mirrors_lepy/vedo
## Basic Information
- **Project Name**: vedo
- **Description**: A python module for scientific analysis of 3D data
- **Primary Language**: Unknown
- **License**: MIT
- **Default Branch**: master
- **Homepage**: None
- **GVP Project**: No
## Statistics
- **Stars**: 0
- **Forks**: 0
- **Created**: 2022-08-10
- **Last Updated**: 2025-09-28
## Categories & Tags
**Categories**: Uncategorized
**Tags**: None
## README

[](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/MIT_License)
[](https://anaconda.org/conda-forge/vedo)
[](https://repology.org/project/vedo/versions)
[](https://doi.org/10.5281/zenodo.5842090)
[](https://pepy.tech/project/vedo)
[](https://circleci.com/gh/marcomusy/vedo)
A lightweight and powerful python module
for scientific analysis and **v**isualization of **3d** **o**bjects.
### ✨ Philosophy
Inspired by the *vpython* *manifesto* "3D programming for ordinary mortals",
`vedo` makes it easy to work with 3D pointclouds, meshes and volumes,
in just a few lines of code, even for less experienced programmers.
`vedo` is based on [VTK](https://www.vtk.org/) and [numpy](http://www.numpy.org/),
with no other dependencies.
## 💾 Installation
```bash
pip install vedo
```
additional installation details [click to expand]
- To install the latest _dev_ version of `vedo`:
`pip install -U git+https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo.git`
- To install from the conda-forge channel:
`conda install -c conda-forge vedo`
## 📙 Documentation
The webpage of the library with documentation is available [**here**](https://vedo.embl.es).
📌 **Need help? Have a question, or wish to ask for a missing feature?**
Do not hesitate to ask any questions on the [**image.sc** forum](https://forum.image.sc/)
or by opening a [**github issue**](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/issues).
## 🎨 Features
The library includes a [large set of working examples](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples)
for a wide range of functionalities:
working with polygonal meshes and point clouds [click to expand]
- Import meshes from VTK format, STL, Wavefront OBJ, 3DS, Dolfin-XML, Neutral, GMSH, OFF, PCD (PointCloud),
- Export meshes as ASCII or binary to VTK, STL, OBJ, PLY ... formats.
- Analysis tools like Moving Least Squares, mesh morphing and more..
- Tools to visualize and edit meshes (cutting a mesh with another mesh, slicing, normalizing, moving vertex positions, etc..).
- Split mesh based on surface connectivity. Extract the largest connected area.
- Calculate areas, volumes, center of mass, average sizes etc.
- Calculate vertex and face normals, curvatures, feature edges. Fill mesh holes.
- Subdivide faces of a mesh, increasing the number of vertex points. Mesh simplification.
- Coloring and thresholding of meshes based on associated scalar or vectorial data.
- Point-surface operations: find nearest points, determine if a point lies inside or outside of a mesh.
- Create primitive shapes: spheres, arrows, cubes, torus, ellipsoids...
- Generate glyphs (associate a mesh to every vertex of a source mesh).
- Create animations easily by just setting the position of the displayed objects in the 3D scene. Add trailing lines and shadows to moving objects is supported.
- Straightforward support for multiple sync-ed or independent renderers in the same window.
- Registration (alignment) of meshes with different techniques.
- Mesh smoothing.
- Delaunay triangulation in 2D and 3D.
- Generate meshes by joining nearby lines in space.
- Find the closest path from one point to another, traveling along the edges of a mesh.
- Find the intersection of a mesh with lines, planes or other meshes.
- Interpolate scalar and vectorial fields with Radial Basis Functions and Thin Plate Splines.
- Add sliders and buttons to interact with the scene and the individual objects.
- Visualization of tensors.
- Analysis of Point Clouds:
- Moving Least Squares smoothing of 2D, 3D and 4D clouds
- Fit lines, planes, spheres and ellipsoids in space
- Identify outliers in a distribution of points
- Decimate a cloud to a uniform distribution.
working with volumetric data and tetrahedral meshes
- Import data from VTK format volumetric TIFF stacks, DICOM, SLC, MHD and more
- Import 2D images as PNG, JPEG, BMP
- Isosurfacing of volumes
- Composite and maximum projection volumetric rendering
- Generate volumetric signed-distance data from an input surface mesh
- Probe volumes with lines and planes
- Generate stream-lines and stream-tubes from vectorial fields
- Slice and crop volumes
- Support for other volumetric structures (structured and grid data)
plotting and histogramming in 2D and 3D
- Polygonal 3D text rendering with Latex-like syntax and unicode characters, with 14 different fonts.
- Fully customizable axis styles
- donut plots and pie charts
- Scatter plots in 2D and 3D
- Surface function plotting
- 1D customizable histograms
- 2D hexagonal histograms
- Polar plots, spherical plots and histogramming
- Draw latex-formatted formulas in the rendering window.
- Quiver, violin, whisker and stream-line plots
- Graphical markers analogous to matplotlib
integration with other libraries
- Integration with the [Qt5](https://www.qt.io/) framework.
- Support for [FEniCS/Dolfin](https://fenicsproject.org/) platform for visualization of PDE/FEM solutions.
- Interoperability with the [trimesh](https://trimsh.org/), [pyvista](https://github.com/pyvista/pyvista) and [pymeshlab](https://github.com/cnr-isti-vclab/PyMeshLab) libraries.
- Export 3D scenes and embed them into a [web page](https://vedo.embl.es/examples/fenics_elasticity.html).
- Embed 3D scenes in *jupyter* notebooks with [K3D](https://github.com/K3D-tools/K3D-jupyter) (can export an interactive 3D-snapshot page [here](https://vedo.embl.es/examples/geo_scene.html)).
### ⌨ Command Line Interface
Visualize a polygonal mesh or a volume from a terminal window simply with:
```bash
vedo https://vedo.embl.es/examples/data/embryo.tif
```
Volumetric files (_mhd, vti, slc, tiff, DICOM etc.._) can be visualized in different modes:
|Volume 3D slicing
`vedo --slicer embryo.slc`| Ray-casting
`vedo -g`| 2D slicing
`vedo --slicer2d`| Colorize voxels
`vedo --lego`|
|:--------|:-----|:--------|:-----|
| 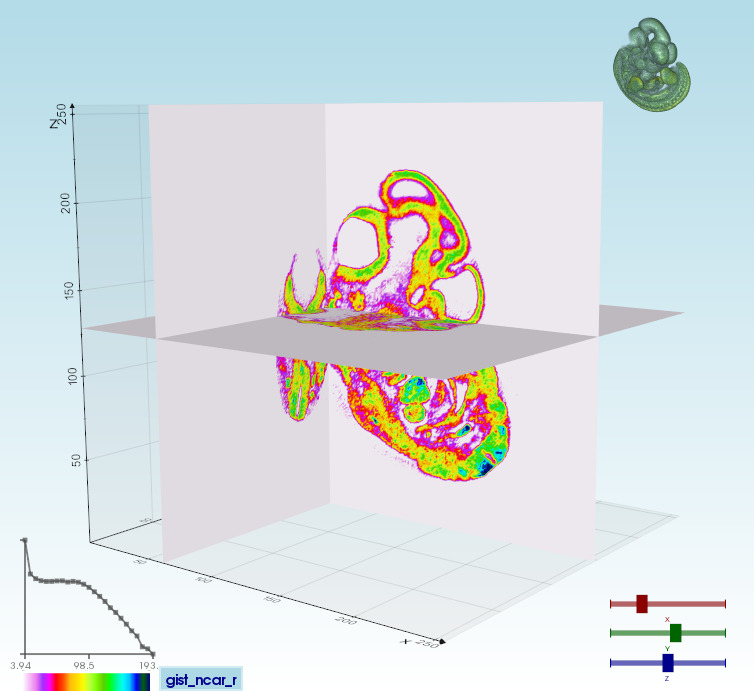|| |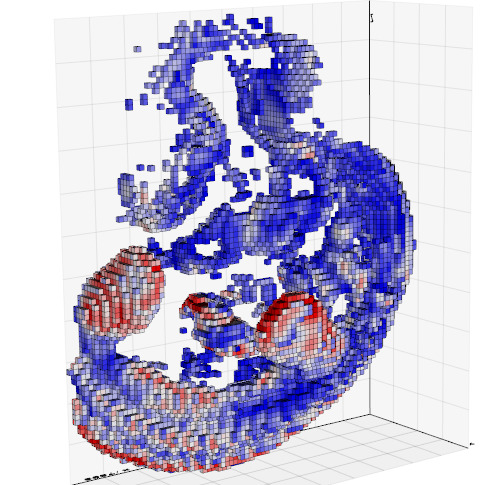 |
Type `vedo -h` for the complete list of options.
## 🐾 Gallery
`vedo` currently includes 300+ working [examples](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples) and [notebooks](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/notebooks).
||||
|:--------|:--------|:--------|
| [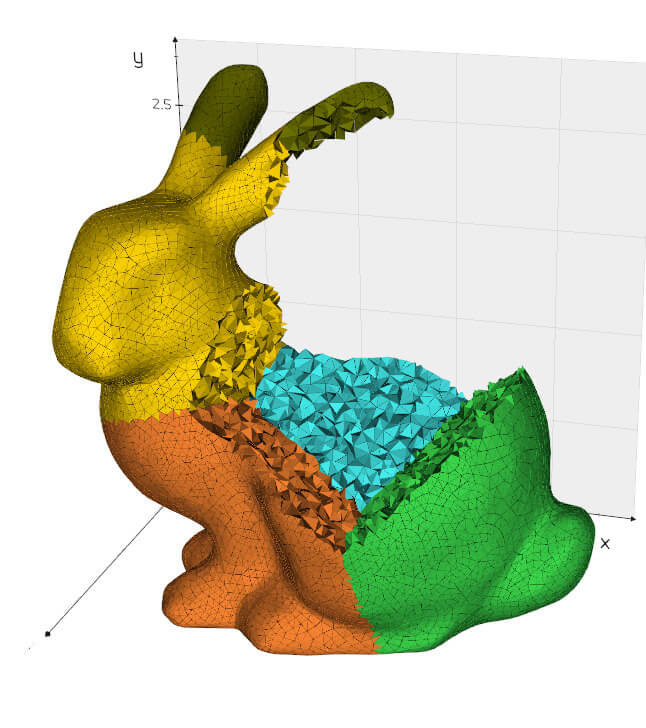](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/blob/master/examples/volumetric/tetralize_surface.py) | [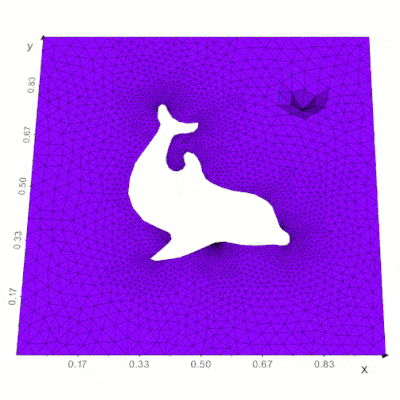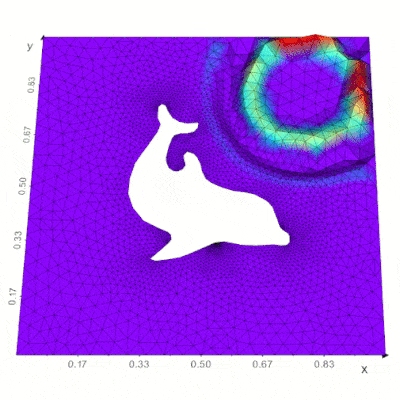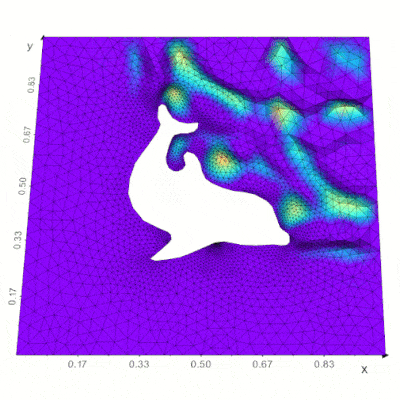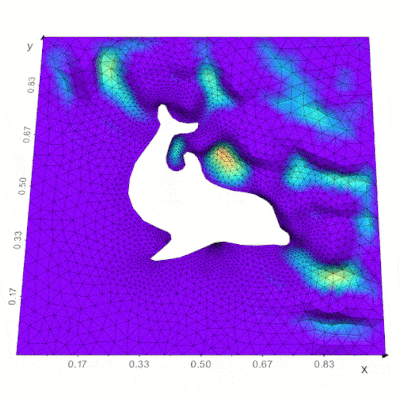](https://vedo.embl.es/content/vedo/dolfin.html) | [](https://github.com/marcomusy/vedo/tree/master/examples/simulations/grayscott.py) |
| *Work with volumes, tetrahedral and polygonal meshes.* | *Interoperability with many external libraries* | *Animations of physical systems* |
Run any of the built-in examples. In a terminal type: `vedo -r earthquake_browser`
Check out the example galleries organized by subject here:

## ✏ Contributing
Any contributions you make are **greatly appreciated**!
If you have a suggestion that would make this better, please fork the repo and create a pull request.
You can also simply open an issue with the tag "enhancement".
## 📜 References
**Scientific publications leveraging `vedo`:**
- X. Diego *et al.*:
*"Key features of Turing systems are determined purely by network topology"*,
Phys. Rev. X 8, 021071,
[DOI](https://journals.aps.org/prx/abstract/10.1103/PhysRevX.8.021071).
- M. Musy, K. Flaherty *et al.*:
*"A Quantitative Method for Staging Mouse Limb Embryos based on Limb Morphometry"*,
Development (2018) 145 (7): dev154856,
[DOI](http://dev.biologists.org/content/145/7/dev154856).
- F. Claudi, A. L. Tyson, T. Branco, *"Brainrender. A python based software for visualisation
of neuroanatomical and morphological data."*,
eLife 2021;10:e65751,
[DOI](https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.65751).
- J. S. Bennett, D. Sijacki,
*"Resolving shocks and filaments in galaxy formation simulations: effects on gas properties and
star formation in the circumgalactic medium"*,
Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society, Volume 499, Issue 1,
[DOI](https://doi.org/10.1093/mnras/staa2835).
- J.D.P. Deshapriya *et al.*,
*"Spectral analysis of craters on (101955) Bennu"*.
Icarus 2020,
[DOI](https://doi.org/10.1016/j.icarus.2020.114252).
- A. Pollack *et al.*,
*"Stochastic inversion of gravity, magnetic, tracer, lithology, and fault data
for geologically realistic structural models: Patua Geothermal Field case study"*,
Geothermics, Volume 95, September 2021,
[DOI](https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geothermics.2021.102129).
- X. Lu *et al.*,
*"3D electromagnetic modeling of graphitic faults in the Athabasca
Basin using a finite-volume time-domain approach with unstructured grids"*,
Geophysics,
[DOI](https://doi.org/10.1190/geo2020-0657.1).
- M. Deepa Maheshvare *et al.*,
*"A Graph-Based Framework for Multiscale Modeling of Physiological Transport"*,
Front. Netw. Physiol. 1:802881,
[DOI](https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnetp.2021.802881/full).
- F. Claudi, T. Branco,
*"Differential geometry methods for constructing manifold-targeted recurrent neural networks"*,
bioRxiv 2021.10.07.463479,
[DOI](https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.10.07.463479).
- J. Klatzow, G. Dalmasso, N. Martínez-Abadías, J. Sharpe, V. Uhlmann,
*"µMatch: 3D shape correspondence for microscopy data"*,
Front. Comput. Sci., 15 February 2022.
[DOI](https://doi.org/10.3389/fcomp.2022.777615)
- G. Dalmasso *et al.*, *"4D reconstruction of developmental trajectories using spherical harmonics"*,
bioRxiv 2021.12.16.472948,
[DOI](https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.12.16.472948).
**Have you found this software useful for your research? Star ✨ the project and cite it as:**
M. Musy et al.,
"vedo, a python module for scientific analysis and visualization of 3D objects and point clouds",
Zenodo, 2021, doi: 10.5281/zenodo.5842090.
[](https://www.embl.es)