# deep_learning_NLP
**Repository Path**: quarky/deep_learning_NLP
## Basic Information
- **Project Name**: deep_learning_NLP
- **Description**: No description available
- **Primary Language**: Unknown
- **License**: Not specified
- **Default Branch**: master
- **Homepage**: None
- **GVP Project**: No
## Statistics
- **Stars**: 0
- **Forks**: 0
- **Created**: 2020-01-25
- **Last Updated**: 2021-11-02
## Categories & Tags
**Categories**: Uncategorized
**Tags**: None
## README
# Deep Learning architectures for NLP  
This repository contains Keras, PyTorch and NumPy implementations of some deep learning architectures for NLP. For a quick theoretical intro about Deep Learning for NLP, I encourage you to have a look at my [notes](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1808.09772.pdf).
## Word2vec and doc2vec by hand in NumPy
https://github.com/Tixierae/deep_learning_NLP/blob/master/skipgram/sg_d2v_numpy.ipynb
In this notebook, we learn word and document vectors completely by hand on the IMDB movie review dataset, with just a `for` loop and NumPy! We implement the following models:
* word2vec's **skip-gram with negative sampling**, as introduced in [Efficient Estimation of Word Representations in Vector Space](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1301.3781.pdf) and [Distributed Representations of Words and Phrases and their Compositionality](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1310.4546.pdf).
* doc2vec (a.k.a. Paragraph Vector)'s **distributed bag-of-words**, following [Distributed Representations of Sentences and Documents](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1405.4053.pdf).
We also:
* write an **inference** function to compute the vector of any new document
* **visualize** word and document vectors separately, and together in the same space

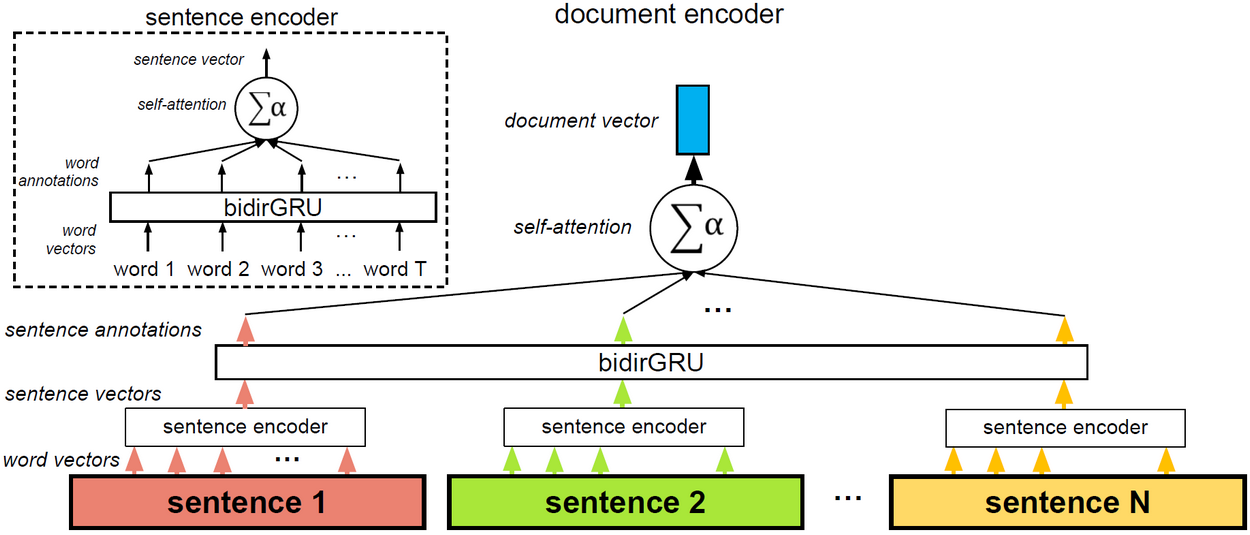
## Hierarchical Attention Network for Document Classification
A **RAM-friendly** implementation of the model introduced by [Yang et al. (2016)](http://www.aclweb.org/anthology/N16-1174), with step-by-step explanations and links to relevant resources: https://github.com/Tixierae/deep_learning_NLP/blob/master/HAN/HAN_final.ipynb
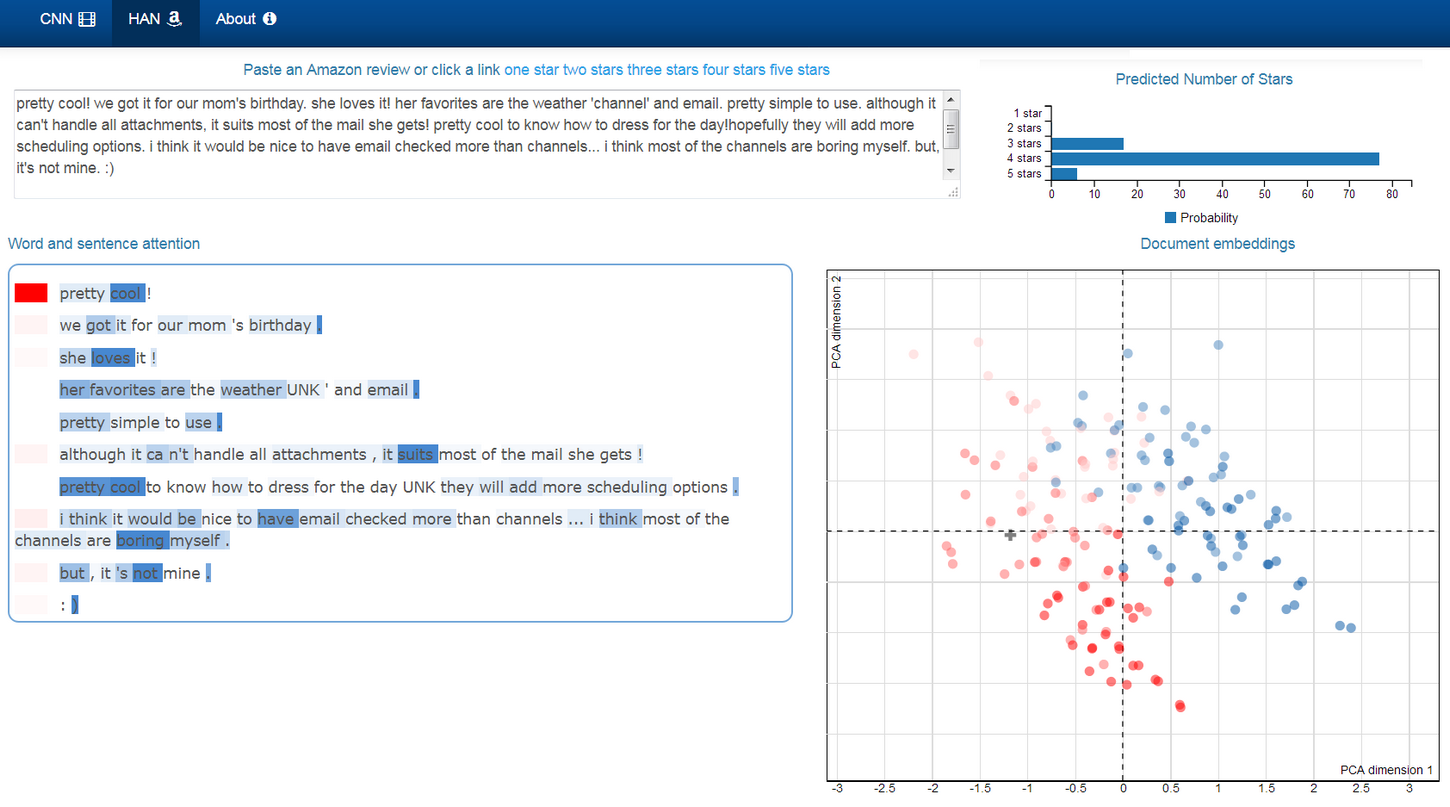
In my experiments on the **Amazon review dataset** (3,650,000 documents, 5 classes), I reach **62.6%** accuracy after 8 epochs, and **63.6%** accuracy (the accuracy reported in the paper) after 42 epochs. Each epoch takes about 20 mins on my TitanX GPU. I deployed the model as a [web app](https://safetyapp.shinyapps.io/DNLPvis/). As shown in the image below, you can paste your own review and visualize how the model pays attention to words and sentences.
### Concepts covered
The notebook makes use of the following concepts:
- **batch training**. Batches are loaded from disk and passed to the model one by one with a generator. This way, it's possible to train on datasets that are too big to fit on RAM.
- **bucketing**. To have batches that are as dense as possible and make the most of each tensor product, the batches contain documents of similar sizes.
- **cyclical learning rate and cyclical momentum schedules**, as in [Smith (2017)](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1506.01186.pdf) and [Smith (2018)](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1803.09820.pdf). The cyclical learning rate schedule is a new, promising approach to optimization in which the learning rate increases and decreases in a pre-defined interval rather than keeping decreasing. It worked better than Adam and SGD alone for me1.
- **self-attention** (aka inner attention). We use the formulation of the original paper.
- **bidirectional RNN**
- **Gated Recurrent Unit (GRU)**
1There is more and more evidence that adaptive optimizers like Adam, Adagrad, etc. converge faster but generalize poorly compared to SGD-based approaches. For example: [Wilson et al. (2018)](https://arxiv.org/pdf/1705.08292.pdf), this [blogpost]( https://shaoanlu.wordpress.com/2017/05/29/sgd-all-which-one-is-the-best-optimizer-dogs-vs-cats-toy-experiment/). Traditional SGD is very slow, but a cyclical learning rate schedule can bring a significant speedup, and even sometimes allow to reach better performance.
## 1D Convolutional Neural Network for short text classification
An implementation of [(Kim 2014)'s](https://arxiv.org/abs/1408.5882) 1D Convolutional Neural Network for short text classification: https://github.com/Tixierae/deep_learning_NLP/blob/master/CNN_IMDB/cnn_imdb.ipynb

## 2D CNN for image classification
Agreed, this is not for NLP. But an implementation can be found here https://github.com/Tixierae/deep_learning_NLP/blob/master/CNN_MNIST/mnist_cnn.py. I reach 99.45% accuracy on MNIST with it.
## Inverted index and TF-IDF by hand
This notebook provides simple functions to clean and index documents, and to execute word and phrase queries. It also show how to compute TF-IDF coefficients.
https://github.com/Tixierae/deep_learning_NLP/blob/master/other/inverted_index_tfidf.ipynb
## Cite
If you use some of the code in this repository in your work, please cite
```BibTeX
@article{tixier2018notes,
title={Notes on Deep Learning for NLP},
author={Tixier, Antoine J.-P.},
journal={arXiv preprint arXiv:1808.09772},
year={2018}
}
```
```
Tixier, A. J. P. (2018). Notes on Deep Learning for NLP. arXiv preprint arXiv:1808.09772.
```


